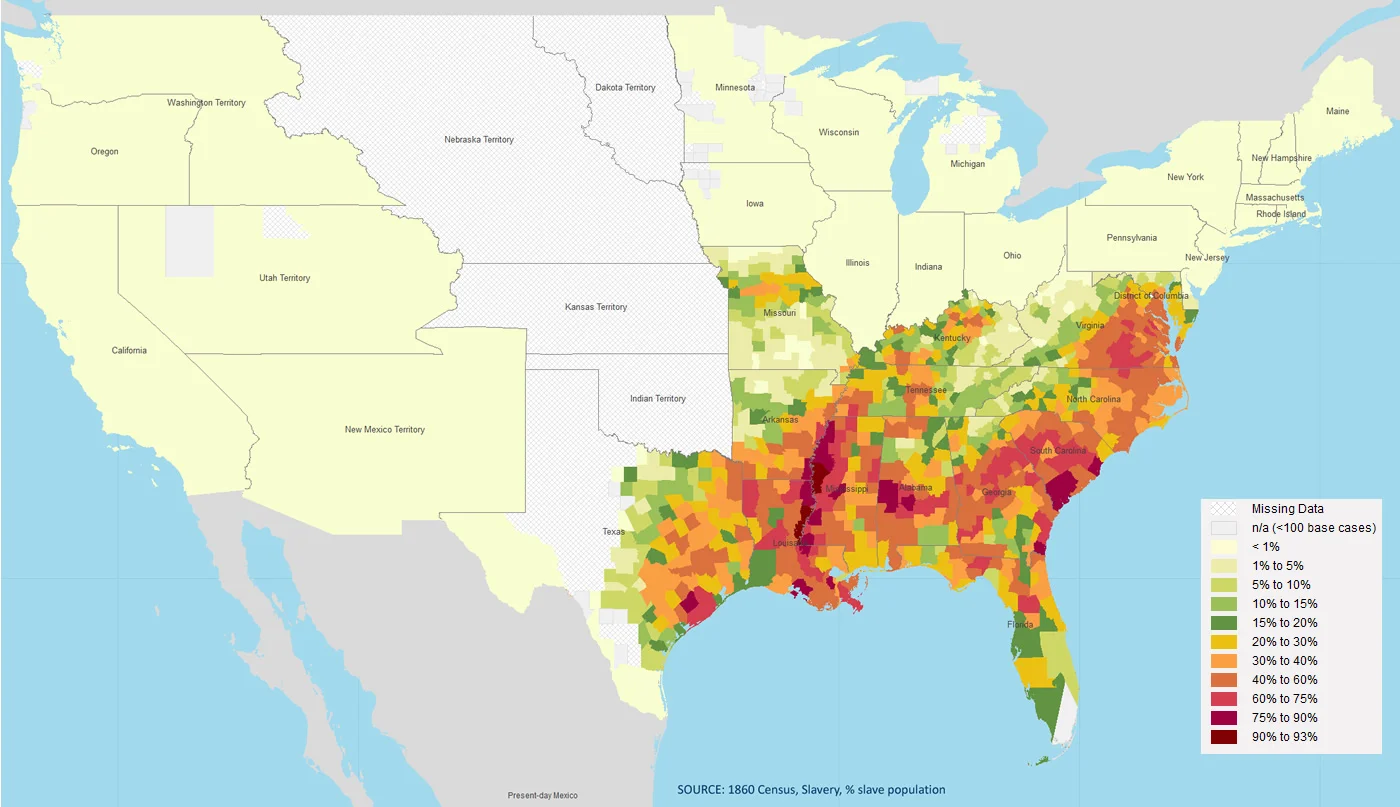
Could Slavery Have Died a Peaceful Death?
/On January 31, 1865, the United States Congress narrowly passed an amendment to the Constitution abolishing slavery; that this was accomplished thanks to the American Civil War is undeniable. That destroying slavery became a primary goal of the Civil War, however, was not initially expected. Many northerners were extremely reluctant to abolish the institution. Only through the actions of enslaved men and women, a small group of abolitionists, and the interaction of U.S. soldiers with the brutal institution was the North compelled to focus on slavery. Which begs the question: Could slavery have been abolished without the Civil War?
Read More